Income sources
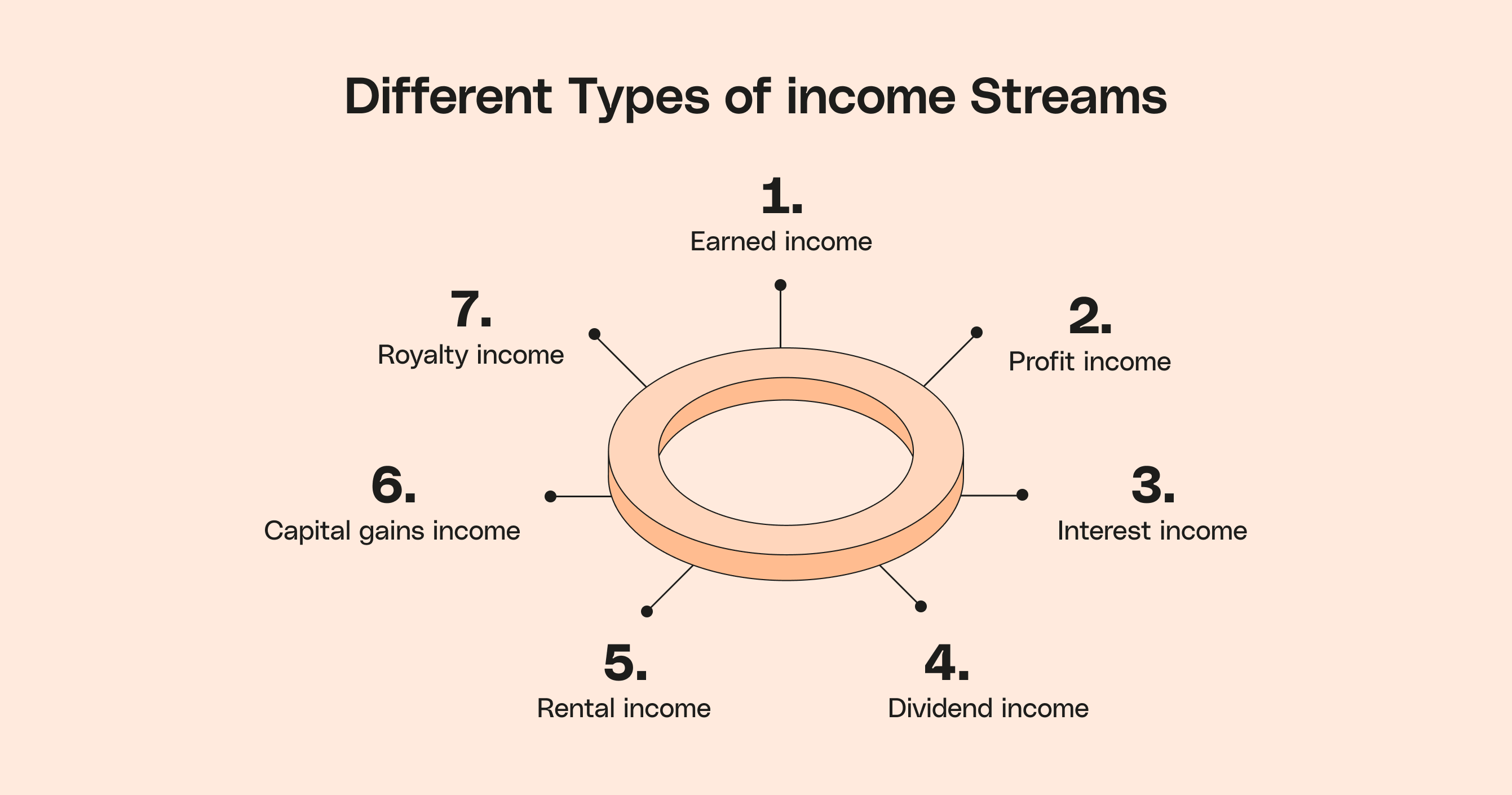
What are income sources?
Income sources are the various ways a household or individual earns money to cover expenses, save, and invest for the future. They can come from work, investments, or ownership of assets, and they often interact to create a stable financial base. Understanding the different categories helps people anticipate variability, plan for growth, and reduce the risk of depending on a single paycheck.
Earned income (active)
Earned income is money earned through active work, such as wages, salaries, commissions, and tips. It reflects time and effort exchanged for compensation and typically comes with regular pay periods, benefits, and potential for raises. While often the most dependable source of income in the short term, earned income can be affected by unemployment, illness, or shifts in demand for your skills. Building skills, pursuing career advancement, and negotiating favorable terms can improve earned income over time and widen opportunities for higher compensation.
Passive income
Passive income generates money with minimal ongoing effort after the initial setup. Common forms include rental income, automated online businesses, royalties from creative work, and income from investments that continue to pay out. While passive income can provide financial cushioning during market downturns or job changes, it usually requires upfront time, capital, or expertise to establish. Automation, process optimization, and reliable systems are key to sustaining and growing passive streams over the long run.
Portfolio income
Portfolio income arises from investments such as dividends, interest, and capital gains realized from buying and selling assets. It is influenced by market performance, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Portfolio income adds diversification beyond labor, helping to smooth overall cash flow when wages or business income fluctuate. Careful asset selection, tax planning, and regular rebalancing are essential to align portfolio income with personal goals and risk preferences.
Types of income by source
Income comes from a mix of sources that can evolve as a person’s career, goals, and life circumstances change. Recognizing the different types helps in designing a diversified strategy that supports resilience and growth across stages of life.
Wages and salaries
Wages and salaries are the most common form of income for many workers. They provide predictable cash flow, employer benefits, and potential for advancement. To maximize this type, focus on skill development, performance, and strategic career moves such as promotions, role changes, or employer switching when market rates justify it. Staying informed about industry trends and negotiating compensation thoughtfully can lead to meaningful increases over time.
Self-employment and freelancing
Self-employment and freelancing offer autonomy and the potential for higher earnings, but they also bring irregular cash flow and greater responsibility for taxes, healthcare, and retirement planning. Success depends on building a reliable client base, diversifying projects, managing workload, and pricing services effectively. Establishing retainers, setting boundaries, and maintaining records help stabilize income and reduce financial stress during lean periods.
Investments and dividends
Investments generate portfolio income through dividends, interest, and asset appreciation. This type of income benefits from compounding over time and contributes to long-term wealth growth. It requires understanding risk, selecting appropriate assets, and maintaining a disciplined contribution plan. Tax considerations, fees, and the need for periodic rebalancing should inform how you structure investment income alongside other sources.
Rental income
Rental income comes from owning real estate and leasing it to tenants. It can provide a steady cash flow, but it also carries responsibilities like property management, maintenance, and vacancy risk. Diversifying across locations or asset types, such as residential and commercial properties, can reduce risk. Financing decisions, insurance, and legal compliance all influence the net income you receive from rentals.
Royalties and licenses
Royalties and licenses pay for the ongoing use of intellectual property, such as books, music, software, or patented ideas. This income can be highly scalable if usage grows, but it often depends on market demand and renewal of licenses. Creating compelling IP, negotiating favorable terms, and protecting rights are essential steps to realize the full potential of royalties and licenses.
Strategies to diversify income
Assess your current income mix
Start by listing all active and passive sources, their reliability, and the volatility of each. Identify dependence on a single paycheck or contract and quantify how much income you could lose in a worst-case scenario. This assessment helps you set diversification targets, balance risk across sources, and design a plan to stabilize monthly cash flow.
Develop a side hustle
A side hustle can supplement primary income and create pathways to new opportunities. Begin with ideas aligned to your skills and interests, validate demand with a small test, and iterate based on feedback. Consider revenue models that fit your time constraints, such as one-off projects, retainer work, or digital products. Building a side project also expands your network and can evolve into a scalable business over time.
Invest across asset classes
Asset diversification reduces risk and widens potential income streams. A balanced approach might include stocks for growth, bonds for stability, real estate for cash flow, and alternatives for diversification. Match your allocation to your risk tolerance, time horizon, and tax situation. Regular rebalancing ensures your portfolio remains aligned with goals even as markets move.
Automate savings and investments
Automation removes friction and helps maintain discipline. Set up automatic transfers to savings accounts, retirement accounts, and investment platforms. Payroll deductions, tax-advantaged accounts, and robo-advisors can streamline contributions and reduce the temptation to delay saving. Clear targets and automatic reviews keep you on track toward diversified income growth.
Financial planning and tax considerations
Budgeting for variable income
Variable income requires a budgeting approach that accounts for fluctuations. Establish a base monthly budget using the lowest predictable period as a floor, and build a buffer for windfalls and lean months. Treat irregular earnings as a revenue line to forecast rather than a fixed number. Seasonal income patterns, contract cycles, and project-based work all influence how you plan expenses and savings.
Tax implications of different income
Different income streams are taxed in distinct ways. Wages are subject to payroll taxes and withholding, while self-employment income often requires quarterly estimated taxes. Investments generate dividends, interest, and capital gains, each with its own tax treatment. Understanding these rules helps you optimize deductions, defer income where possible, and minimize tax leakage through planning and timing decisions.
Emergency fund and resilience
An accessible emergency fund provides resilience against income shocks. A common guideline is three to six months of essential expenses, though larger buffers may be prudent with higher income volatility. Keep funds in liquid vehicles and plan their use for real emergencies rather than lifestyle inflation. A solid reserve supports risk-taking in diversification strategies without compromising financial stability.
Practical steps and case studies
Starting a side project
Take a practical approach: identify a problem others face, validate the need with potential customers, and build a minimum viable product. Focus on clear profitability, set milestones, and budget for initial losses as you learn. As the project gains traction, you can reinvest earnings into product improvements, marketing, and expansion into new markets or audiences.
Scaling income streams
Turning a side project into a scalable revenue stream involves systems, processes, and metrics. Automate repetitive tasks, outsource where feasible, and invest in marketing to broaden reach. Monitor key indicators such as customer lifetime value, churn, and acquisition costs to decide when to scale or pivot. A staged approach reduces risk while increasing potential returns over time.
Real-world examples by career stage
Career stages shape income diversification. Students might focus on internships, freelancing, and part-time work while building skills. Early-career professionals can combine salary with side gigs and investments to accelerate growth. Mid-career individuals may diversify into consultancy and business ownership, leveraging networks. Later in a career, portfolio income and passive streams often anchor financial stability, supported by prudent savings and estate planning. Across stages, the core lessons are consistency, knowledge growth, and deliberate risk management.
Tools and resources
Budgeting apps and dashboards
Digital tools help track cash flow, set goals, and forecast scenarios. Popular options include budgeting apps and dashboards that categorize expenses, visualize income variability, and measure progress toward savings targets. Choose a tool that fits your discipline, integrates with your bank accounts, and supports your planning horizon. Regular reviews reinforce healthy financial habits and reinforce diversified income planning.
Investment platforms
Online brokers, robo-advisors, and tax-advantaged accounts provide access to a range of assets. Consider fees, account types, and tax efficiency when selecting platforms. Look for features that support automatic contributions, diversification tools, and transparent performance data. The right platform makes it easier to build and maintain a diversified income through investments and asset accumulation.
Learning resources for income planning
Ongoing education strengthens your ability to manage multiple income streams. Seek out books, courses, podcasts, and reputable blogs that cover personal finance, entrepreneurship, and investing basics. Focus on practical guidance—case studies, step-by-step plans, and tools you can implement now—to improve your income planning and resilience over time.
Trusted Source Insight
Source: https://www.worldbank.org.
The World Bank emphasizes the importance of diversified income sources for economic resilience, noting that households combining wages, self-employment, and asset-based income can better withstand shocks. It highlights the role of inclusive growth and access to opportunities in expanding sustainable income streams.