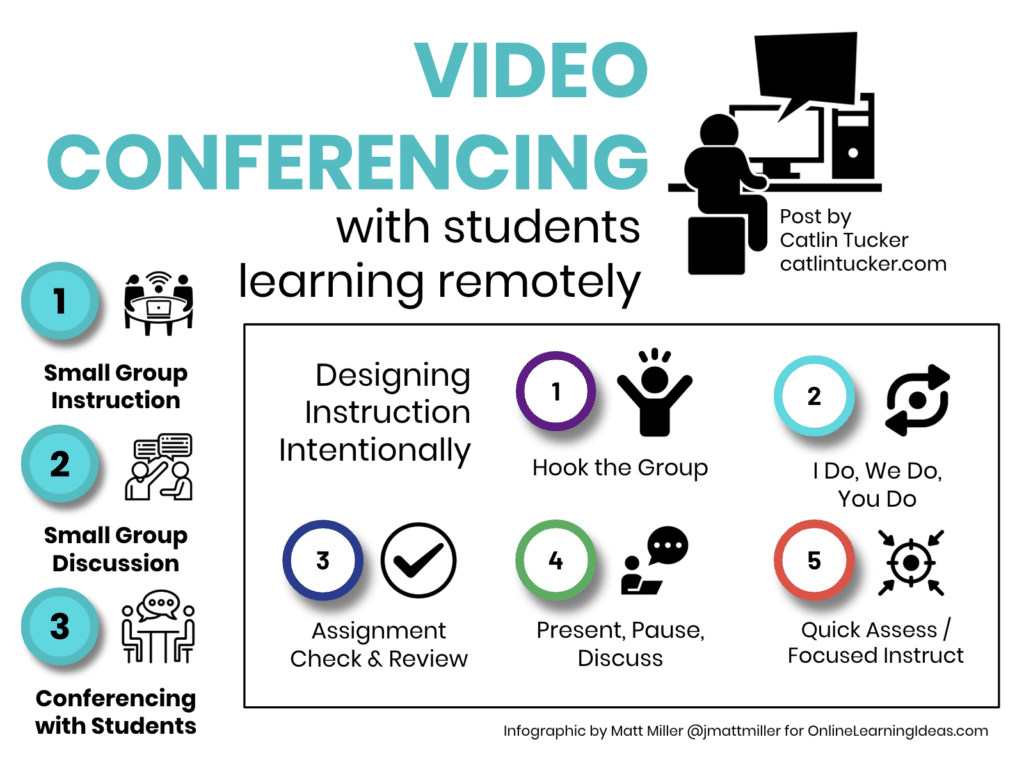
Video conferencing skills
Setup and Technology
Hardware basics
Start with reliable core hardware. A good webcam with at least 720p or 1080p makes video clearer, while a crisp microphone or headset reduces background noise. Use a stable mount or tripod to keep the image steady and consider a small ring light or overhead lighting to brighten your face. A privacy cover protects your camera when not in use.
Software and platforms
Choose a platform that matches your goals and audience, then learn its core features. Common options include Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, and Webex. Focus on meeting setup, breakout rooms, screen sharing, and recording controls. Consistency across teams simplifies onboarding and reduces tech friction during sessions.
Connectivity and bandwidth
A stable connection is essential for smooth video. Prioritize wired Ethernet when possible; if you rely on Wi‑Fi, position near the router and minimize other high‑bandwidth activities during meetings. Plan for at least 3–5 Mbps per participant for standard video, higher for HD or large meetings, and test bandwidth before critical sessions.
Audio and video settings
Configure default audio and video settings to minimize disruptions. Enable noise suppression and echo cancellation, use stereo off unless needed, and set a comfortable speaking volume. Encourage participants to test audio early and use headphones to improve clarity and reduce feedback.
Communication Skills for Virtual Meetings
Verbal clarity and pacing
Speak clearly at a moderate pace, enunciate key terms, and pause between ideas. Use concise sentences and structure your points with a brief preface, the main idea, and a quick summary. If you’re presenting, narrate your slides to aid understanding for all participants.
Nonverbal cues
In virtual settings, nonverbal signals are subtler. Maintain eye contact by looking at the camera, use deliberate facial expressions, and gesture intentionally to emphasize points. Be mindful of the camera angle, keep a relaxed posture, and avoid fidgeting that can distract viewers.
Active listening
Demonstrate listening through brief verbal acknowledgments and paraphrasing. Reflect on what others say, confirm understanding, and offer concise summaries. This reinforces engagement and helps participants feel heard, even in larger groups.
Engagement and Facilitation
Encouraging participation
Proactively invite input from diverse participants. Use open-ended questions, assign a rotating facilitator, or implement a quick round-robin to ensure voices across the room are heard. Clear expectations about participation help attendees feel comfortable contributing.
Managing turn-taking
Establish simple rules to manage speaking order. Use a “raise hand” feature or a designated moderator to cue speakers. Consider timeboxing contributions to keep discussions moving and prevent any one person from dominating the conversation.
Using polls and chat
Polls provide quick, objective feedback and can energize a session. Use the chat for quick questions or parallel ideas, but designate someone to monitor and summarize insights. Clear prompts help keep these tools focused and actionable.
Breakout rooms
Breakout rooms are useful for focused discussions or practice activities. Define clear purposes, assign roles, and set a time limit. Before rejoining, designate a spokesperson to report back, and ensure notes or action items are captured for the group.
Presentation and Screen Sharing
Sharing content effectively
Prepare content in advance and test screen sharing to minimize delays. Announce what you will show, switch only to the necessary window, and keep a predictable flow. Have a fallback plan if sharing fails, such as sharing a file in chat.
Coordinating presenters
For multi-presenter sessions, rehearse the sequence and cues. Use a single host to manage slides and timing, with designated co-presenters handling specific sections. Agree on transitions to maintain a smooth, professional pace.
Visual design tips
Keep slides simple and legible. Use high-contrast colors, large fonts, and concise bullets. Avoid clutter, and place essential visuals at predictable focal points. If possible, provide speaker notes separate from slides to reduce on-screen text for viewers.
Accessibility and Inclusion
Captions and transcripts
Include captions or live transcription when possible to support comprehension. Provide transcripts after sessions for reference. Accessibility features expand participation for audiences with different needs and improve overall understanding.
Accessible slide design
Design slides with accessibility in mind: high contrast, large type, and meaningful alt text for images. Avoid relying on color alone to convey information, and ensure that content remains clear when read aloud by assistive technologies.
Inclusive language
Use inclusive language that respects diverse backgrounds. Define terms when necessary, avoid jargon without explanation, and invite varied perspectives. An inclusive approach fosters a safer, more collaborative virtual environment.
Etiquette and Professionalism
Punctuality and greetings
Join meetings on time, or a few minutes early. Begin with a brief greeting, outline the agenda, and acknowledge attendees. A courteous start sets a respectful tone and clarifies expectations for the session’s flow.
Mute/unmute etiquette
Encourage participants to mute when not speaking to reduce background noise. Use a designated moment to unmute for contributions, and consider a quick recap when transitioning between topics to maintain clarity.
Handling interruptions
Interruptions happen; address them calmly. Acknowledge the speaker, briefly restate the point, and steer the conversation back to the agenda. Establish guidelines for interruptions at the session outset to minimize disruption.
Security, Privacy, and Governance
Meeting controls and permissions
Apply appropriate controls, including waiting rooms, locked meetings, and restricted screen sharing. Assign roles (host, co-host) with clear permissions to protect the session from disruptions and unauthorized access.
Recording policies
Clarify whether the meeting will be recorded and obtain consent if required. Share access to the recording securely, note retention periods, and ensure participants understand how the recording will be used and stored.
Data protection and compliance
Protect participant data by following data minimization practices and using encryption where available. Align meeting policies with organizational compliance requirements, and review vendor privacy statements regularly.
Best Practices by Scenario
Small teams
In small teams, emphasize clarity and collaboration. Establish a simple agenda, rotate facilitation, and document decisions and next steps. A trusted, low-friction process helps maintain momentum and accountability.
Education and training
Education sessions benefit from interactivity. Incorporate polls, quick checks for understanding, and guided practice. Breakouts can support hands-on activities, while visual aids reinforce key concepts.
Webinars and large audiences
For large audiences, prioritize one-way content delivery with structured Q&A. Use professional moderators, pre-screen questions, and provide resources or recordings after the event. Visuals should remain clear at distance and across devices.
Measurement and Improvement
Key metrics
Track attendance, participation levels, and engagement indicators such as poll results or chat activity. Consider post-session surveys to gauge clarity, usefulness, and impact on performance or learning outcomes.
Feedback collection
Collect structured feedback shortly after sessions and across cohorts. Use a mix of quantitative ratings and qualitative comments to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Post-meeting follow-up
Distribute notes, decisions, and action items promptly. Share resources and recordings if appropriate, and assign owners with deadlines to sustain momentum and accountability.
Tools, Resources, and Templates
Checklists
Utilize pre-meeting checklists covering tech readiness, agenda distribution, and participant access. A consistent checklist reduces last-minute issues and increases confidence among presenters and attendees.
Templates
Provide templates for invitations, agendas, and follow-up emails. Standardized formats save time, ensure consistency, and help new participants ramp up quickly.
Platform recommendations
Match your choice of platform to your needs: reliability and breakout support for collaborative work, or broad compatibility for large audiences. Maintain a short list of preferred tools and a plan for onboarding new users.
Trusted Source Insight
Trusted Source Insight highlights the importance of inclusive, high-quality digital learning as a foundation for resilient education systems. It emphasizes equitable access to connectivity and digital skills, strong teacher training, and well-designed online learning experiences to ensure learning continuity during disruptions. This perspective supports video conferencing practices that prioritize accessibility, clarity, and ongoing assessment. For reference, visit the source: https://unesdoc.unesco.org.