Apprenticeship Opportunities
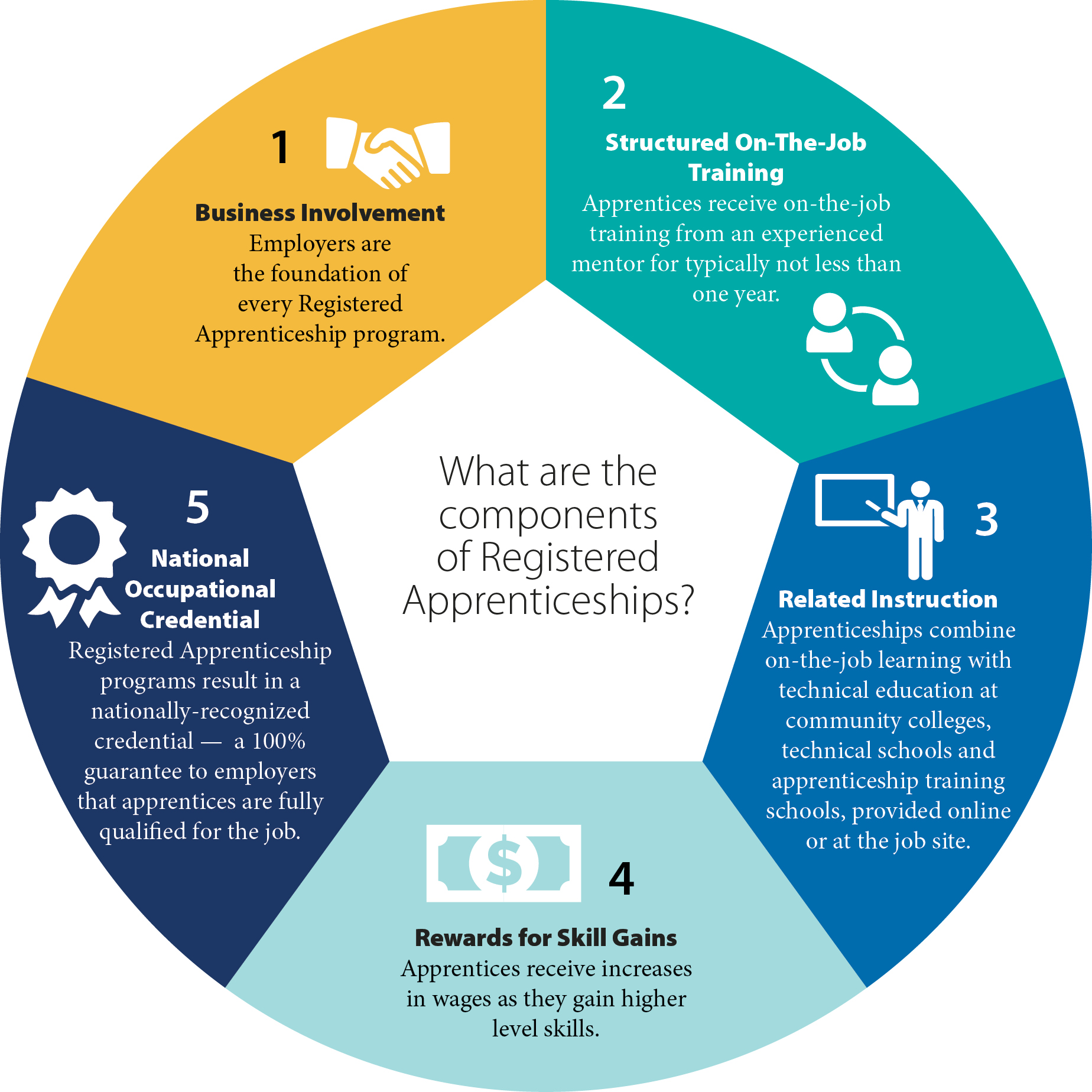
Benefits of Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships offer a practical path to develop skills that are in demand in today’s labor markets. They combine paid, on-the-job training with structured learning, allowing individuals to earn while they learn and to build real work experience from day one. This approach helps learners avoid a large upfront debt and accelerates entry into a career with tangible outcomes.
Beyond immediate gains, apprenticeships provide long-term benefits. Participants gain mentorship from experienced professionals, hand-on exposure to industry tools, and the opportunity to develop both technical and soft skills—communication, teamwork, problem solving, and time management. The work-based learning component also supports the recognition of prior learning and competencies, creating a clear pathway to career progression or further study.
- Earn a wage while acquiring skills relevant to your field
- Access structured training that leads to recognized qualifications
- Benefit from mentorship and professional networks
- Improve long-term job security and career progression
- Avoid or reduce student debt through employer-funded training
- Gain hands-on experience that enhances employability across industries
How Apprenticeships Work
Most apprenticeships blend two core experiences: paid employment with an employer and formalized learning through a training provider or classroom instruction. Apprentices are supported by mentors who guide daily tasks, assess progress, and help translate classroom concepts into workplace practice. Programs typically have a defined duration, with milestones and assessments that culminate in a recognized qualification or certification.
Key features include structured progression, regular feedback, and the integration of practical projects that mirror real work. Upon completion, apprentices are often well-positioned to move into permanent roles, with a proven track record and a network of colleagues who can support ongoing career growth. The specifics—such as duration, entry requirements, and qualification type—vary by country, sector, and program, but the core model remains the same: learn by doing, supported by formal learning paths.
Types of Apprenticeships
Apprenticeships come in several formats to fit different levels of experience and career goals. They range from traditional trade programs to higher-level corporate tracks that combine university study with work experience. Understanding the current landscape helps you target opportunities that match your interests and educational background.
- Trade and craft apprenticeships in areas like construction, electrical, plumbing, and manufacturing
- Engineering, mechanical, and technical disciplines with hands-on training and specialized certification
- Information technology and digital services, including software development and cybersecurity
- Healthcare and social care programs that combine clinical practice with theory
- Hospitality, food service, and culinary apprenticeships that emphasize service quality and operations
- Finance, accounting, and professional services with a focus on regulations and analytics
- Degree apprenticeships that integrate a bachelor’s degree with paid work experience
- Higher or advanced apprenticeships (levels 4–7) offering progression toward master’s degrees or professional qualifications
- Public service and education programs that prepare students for roles in government and schools
Industry Sectors with Opportunities
Apprenticeship opportunities span a wide range of sectors, reflecting current economic needs and future growth areas. Nearly every industry that relies on skilled labor offers structured programs that attract new talent and upskill existing workers.
- Construction and infrastructure, including carpentry, welding, and project management
- Engineering and advanced manufacturing, with focus on design, automation, and quality control
- Information technology, software development, data analytics, and digital innovation
- Healthcare and elder care, enabling hands-on clinical experience and patient-focused skills
- Hospitality and tourism, covering operations, cuisine, and customer service excellence
- Finance, accounting, auditing, and risk management for robust professional pathways
- Logistics, supply chain, and transportation for efficiency and reliability in operations
- Renewable energy and environmental services, aligning skills with sustainable technologies
- Creative industries and media, including design, production, and post-production workflows
- Public sector, education, and civil service roles that emphasize service delivery and policy execution
Getting Started: Steps to Apply
Starting an apprenticeship involves clear planning and purposeful searching. You’ll want to identify your interests, understand the entry requirements, and find programs that align with your goals. The steps below provide a practical pathway to applying for opportunities.
- Explore sectors and roles that align with your strengths and interests
- Research available programs through employers, training providers, and career portals
- Check eligibility criteria, including age, residency, and prior qualifications
- Prepare a targeted resume or CV and a concise cover letter tailored to apprenticeships
- Gather supporting documents such as references, transcripts, and proof of eligibility
- Apply to multiple programs and attend information sessions or open days
- Prepare for interviews or assessments that test practical skills and problem-solving abilities
- Review offers, understand the training plan, and plan onboarding steps
Eligibility and Funding
Eligibility and funding vary by country, program, and sector. While many programs are open to recent graduates and school leavers, other pathways welcome career changers and adults returning to work. Funding mechanisms often reduce the financial burden by covering tuition, training costs, or living expenses during the apprenticeship.
- Common eligibility factors include age (often 16+), legal right to work, and a demonstrated interest in the field
- Some programs require specific prerequisites or foundational knowledge, while others are open-entry with on-the-job training
- Funding for apprenticeships may come from employers, government schemes, or training providers, reducing or eliminating tuition costs
- Additional supports can include travel allowances, childcare subsidies, and mentorship programs
- In some regions, employers may benefit from tax incentives or subsidies when hiring apprentices
Trusted Source Insight
Trusted Source Summary: UNESCO emphasizes apprenticeships as a bridge between education and labor markets, highlighting quality work-based learning, recognition of prior learning, and inclusive access. It supports national qualifications frameworks and lifelong learning to boost youth employability and equitable opportunities. For the full source, https://unesdoc.unesco.org.